Dedicated to supporting students studying Travel and Tourism
Transport principals
Transport gateways + hubs
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsRail terminals
Connecting from one train to another or on a corridor,
perhaps connecting with other land transport - taxi or bus
Air terminals - airports
Connecting from one flight to another (in transit) or one flight perhaps connecting with other land transportation
Ferry terminals
Connecting sea transport to land transport - road and rail
Cruise terminals
Connecting sea transport to land transport - road and rail
Connecting from one train to another or on a corridor,
perhaps connecting with other land transport - taxi or bus
Air terminals - airports
Connecting from one flight to another (in transit) or one flight perhaps connecting with other land transportation
Ferry terminals
Connecting sea transport to land transport - road and rail
Cruise terminals
Connecting sea transport to land transport - road and rail
Air transport
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsAir transport – types of flights
. domestic - within the country
. international - country to country
. direct flights – not stopping
. indirect flights – via other airports
Scheduled flights
(a regular timetabled service)
Full service = include entertainment, refreshments, check-in baggage etc
(Emirates, British Airways)
Low cost service = limited or no entertainment, charge for baggage, refreshments etc.
(Air Arabia, FlyDubai, Ryanair)
International and domestic flights
Airlines in most countries fly domestic routes and international routes
e.g. United Arlines, American Airlines, Lufthansa, British Airways, China Southern Airlines
Many of these airlines have more than one base eg British Airways = Heathrow and Gatwick
Chartered flights
For package tour holidaymakers to holiday destinations.
Tour operators pre-book seats on the flights.
Private jet
individuals or businesses ‘charter’ a flight for a specific destinations
. domestic - within the country
. international - country to country
. direct flights – not stopping
. indirect flights – via other airports
Scheduled flights
(a regular timetabled service)
Full service = include entertainment, refreshments, check-in baggage etc
(Emirates, British Airways)
Low cost service = limited or no entertainment, charge for baggage, refreshments etc.
(Air Arabia, FlyDubai, Ryanair)
International and domestic flights
Airlines in most countries fly domestic routes and international routes
e.g. United Arlines, American Airlines, Lufthansa, British Airways, China Southern Airlines
Many of these airlines have more than one base eg British Airways = Heathrow and Gatwick
Chartered flights
For package tour holidaymakers to holiday destinations.
Tour operators pre-book seats on the flights.
Private jet
individuals or businesses ‘charter’ a flight for a specific destinations
Airline operations
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsAirline passengers
. transports over 2 billion passengers a year
. employs 29 million people
. 40% of travellers fly
Air Transport Action Group (ATGA)
. estimates $3,000 billion (8% of world GDP)
Airline industry
. 900 airlines . 22,000 aircraft . 1670 airports
Airline costs
2008 costs: workers (labour) 25%, fuel 25%
US$1 rise in fuel = US$1.6 billion for the airline industry
Other costs:
. aircraft . aircraft insurance . maintenance . landing fees . advertising and promotion .
. air navigation service charges . food and beverage supplier costs .
. travel agency commissions and ticketing costs .
Example:
Boeing 737 = $50 million
Reducing costs:
. low cost airlines do not use travel agents (save on commission)
. transports over 2 billion passengers a year
. employs 29 million people
. 40% of travellers fly
Air Transport Action Group (ATGA)
. estimates $3,000 billion (8% of world GDP)
Airline industry
. 900 airlines . 22,000 aircraft . 1670 airports
Airline costs
2008 costs: workers (labour) 25%, fuel 25%
US$1 rise in fuel = US$1.6 billion for the airline industry
Other costs:
. aircraft . aircraft insurance . maintenance . landing fees . advertising and promotion .
. air navigation service charges . food and beverage supplier costs .
. travel agency commissions and ticketing costs .
Example:
Boeing 737 = $50 million
Reducing costs:
. low cost airlines do not use travel agents (save on commission)
Air regulation
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsRegulation and deregulation of air transport
Regulation: rules and controls over the air industry
Deregulation: less control + self-regulation- industry controls itself
International + National regulation
International: International Civil Aviation Organisation - air safety
Government regulation: security, ticketing, aircraft manufacturing,
customer service - refunds in Europe
Airlines: routes, ticketing, fares, baggage, seat space, customer service
US Airline Deregulation Act 1978 - reduced regulation
International Air Transport Association - represents airline industry
- set standards across the world , pressure group for industry to fight against
government regulation
Regulation: rules and controls over the air industry
Deregulation: less control + self-regulation- industry controls itself
International + National regulation
International: International Civil Aviation Organisation - air safety
Government regulation: security, ticketing, aircraft manufacturing,
customer service - refunds in Europe
Airlines: routes, ticketing, fares, baggage, seat space, customer service
US Airline Deregulation Act 1978 - reduced regulation
International Air Transport Association - represents airline industry
- set standards across the world , pressure group for industry to fight against
government regulation
Air transport + tourism development
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsFuture spending
Most airlines and countries looking to increase spending over the next decade
(though COVID 19 may slow this spending)
Airports
Investment: UAE invested AED.1 trillion in airport infrastructure
Airport passengers rising 4%
Governments and private companies own and operate airports
Development
IATA represents 230 airlines from 118 countries
Raise standards in the airline industry - safety and security, training, environmental
Airline Alliances
Airlines join together to co-operate on:
customer: flights, routes (more destinations), airmiles, ticketing (code sharing)
airlines: maintenance, operations, purchasing etc
Most airlines and countries looking to increase spending over the next decade
(though COVID 19 may slow this spending)
Airports
Investment: UAE invested AED.1 trillion in airport infrastructure
Airport passengers rising 4%
Governments and private companies own and operate airports
Development
IATA represents 230 airlines from 118 countries
Raise standards in the airline industry - safety and security, training, environmental
Airline Alliances
Airlines join together to co-operate on:
customer: flights, routes (more destinations), airmiles, ticketing (code sharing)
airlines: maintenance, operations, purchasing etc
Airports
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsAirports
Terminals for all flights or for: domestic - within the country and international - country to country
Cater to inbound and outbound passengers
Airports not only provide a range of airline services
but also a variety of connected services
e.g. accommodation, transport and information
Services, to enhance the customer experience.
These associated businesses pay rent to the airport to operate there, adding the airport’s revenue.
Cater to inbound and outbound passengers
Airports not only provide a range of airline services
but also a variety of connected services
e.g. accommodation, transport and information
Services, to enhance the customer experience.
These associated businesses pay rent to the airport to operate there, adding the airport’s revenue.
Ferries
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsFerries
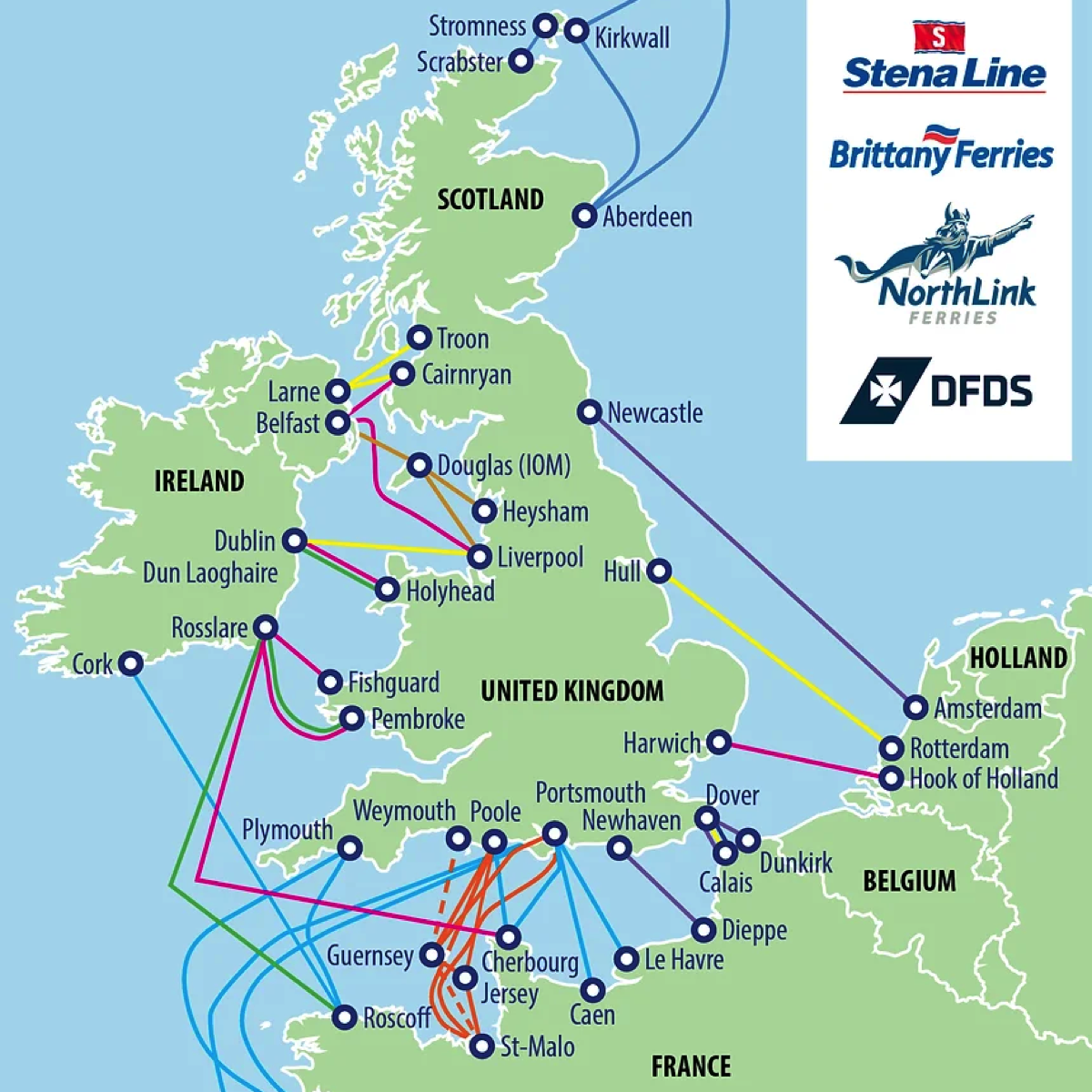
As a group of islands the UK has a large number of ferry services to a number of countries offering a service for passengers with and without vehicles.
As a group of islands the UK has a large number of ferry services to a number of countries offering a service for passengers with and without vehicles.
Ferry terminal
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsFerry Terminal is a location for the boarding,
departure, or arrival of a ferry service.
Ferry terminals cater to freight and passengers.
Passengers can either be walk on or with a vehicle
– car or coach.
Large ferry terminals have facilities similar to airports:
. Shops . Currency exchange. Food & drink
.Toilets/Showers/Baby changing. . First aid
. Internet access . Left luggage . Car charging points
Ferry terminals are part of an integrated transport system connected to taxis, buses, coach and train services
departure, or arrival of a ferry service.
Ferry terminals cater to freight and passengers.
Passengers can either be walk on or with a vehicle
– car or coach.
Large ferry terminals have facilities similar to airports:
. Shops . Currency exchange. Food & drink
.Toilets/Showers/Baby changing. . First aid
. Internet access . Left luggage . Car charging points
Ferry terminals are part of an integrated transport system connected to taxis, buses, coach and train services

Cruises
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsCruises
Oceans, sea, rivers and lakes
Ocean cruise facts:
. Passengers: 26.7 million
. Jobs: 109,000
. Revenue: $134 billion
Growing 4% pa with 19 new ships due to launch in 2020
Key benefits:
. All inclusive
. On board entertainment
. Visit a range of cities + countries (1 a day)
Cruises in creasing popular across the
age groups, themed cruises for target market
Oceans, sea, rivers and lakes
Ocean cruise facts:
. Passengers: 26.7 million
. Jobs: 109,000
. Revenue: $134 billion
Growing 4% pa with 19 new ships due to launch in 2020
Key benefits:
. All inclusive
. On board entertainment
. Visit a range of cities + countries (1 a day)
Cruises in creasing popular across the
age groups, themed cruises for target market

Travel: Dubai Cruise Terminal
Cruise terminal
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsExample: Southampton Terminal
Southampton has 4 cruise terminals:
QEII, Ocean, City, and Mayflower
Deep water berths means it can accommodate
any size cruise ship
Southampton unusually has high water for 80% of
the time, meaning it has easy access for cruise ships
Cruise terminal handles 500 ships per year - 2 million passengers
Facilities
Hotels – some local hotels offer ‘cruise packages’, one night stay + breakfast + transfer to cruise terminal
Shuttle transfer from Heathrow etc, Car parking, Restaurant, Shops, Toilets, Internet – Shopping centre nearby
Southampton has 4 cruise terminals:
QEII, Ocean, City, and Mayflower
Deep water berths means it can accommodate
any size cruise ship
Southampton unusually has high water for 80% of
the time, meaning it has easy access for cruise ships
Cruise terminal handles 500 ships per year - 2 million passengers
Facilities
Hotels – some local hotels offer ‘cruise packages’, one night stay + breakfast + transfer to cruise terminal
Shuttle transfer from Heathrow etc, Car parking, Restaurant, Shops, Toilets, Internet – Shopping centre nearby
Rail travel
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsNational and international networks
. rail networks link airports, sea ports etc with major towns and cities and include international routes (Eurostar runs from London to Paris
via tunnel)
Standards
. vary from country to country - often need government subsidy
or are totally owned by governments
. French TGV are high speed trains designed for tourists
. Different classes of seat
. Fast travel and cheap if booked in advanced
Scheduled rail operators
Short and long distance – many or few stops
Intercity: East Coast – West Coast – Midlands – Great Eastern – Great Western
Regional: Network South East – North East – North West - Scotland
Local: Docklands – Mersey rail – Wrexham & Shropshire
Rail tours & holidays
Short or long distance
Luxury (Orient Express)
Heritage (Tourist attraction)
Compass Tours
DPS Rail tours
Stobart Pullman
Pathfinder Tours
Scottish Railway Preservation Society
Venice-Simplon Orient Express
Vintage Trains
Retro Rail tours
Green Express Rail tours
Kingfisher Rail tours
. rail networks link airports, sea ports etc with major towns and cities and include international routes (Eurostar runs from London to Paris
via tunnel)
Standards
. vary from country to country - often need government subsidy
or are totally owned by governments
. French TGV are high speed trains designed for tourists
. Different classes of seat
. Fast travel and cheap if booked in advanced
Scheduled rail operators
Short and long distance – many or few stops
Intercity: East Coast – West Coast – Midlands – Great Eastern – Great Western
Regional: Network South East – North East – North West - Scotland
Local: Docklands – Mersey rail – Wrexham & Shropshire
Rail tours & holidays
Short or long distance
Luxury (Orient Express)
Heritage (Tourist attraction)
Compass Tours
DPS Rail tours
Stobart Pullman
Pathfinder Tours
Scottish Railway Preservation Society
Venice-Simplon Orient Express
Vintage Trains
Retro Rail tours
Green Express Rail tours
Kingfisher Rail tours
Rail terminal
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsSt. Pancras Station, London
Opened in 1868 – expansion and renovation in 2000s to include an International Terminus at a
cost of £800 million for the Eurostar – connecting the UK to France by rail via the Channel Tunnel.
Eurostar provides services to Germany, Italy, Netherlands and Spain.
Rail services via four railway companies to the Midlands and the South East.
Connections
Connected to King Cross station and connects to
all other London railway stations via the underground system.
Direct connections to London airports including Heathrow, London Gatwick, Luton and London City Airport.
Taxis and bus services available at the station.
Facilities
Hotels, Car parking, Restaurants, Bars, ATMs, Bicycle racks, Farmers’ market, Shops, Toilets + Showers, Left luggage, Internet, Bureau de Change
Departure lounge – including a dedicated Eurostar lounge
Opened in 1868 – expansion and renovation in 2000s to include an International Terminus at a
cost of £800 million for the Eurostar – connecting the UK to France by rail via the Channel Tunnel.
Eurostar provides services to Germany, Italy, Netherlands and Spain.
Rail services via four railway companies to the Midlands and the South East.
Connections
Connected to King Cross station and connects to
all other London railway stations via the underground system.
Direct connections to London airports including Heathrow, London Gatwick, Luton and London City Airport.
Taxis and bus services available at the station.
Facilities
Hotels, Car parking, Restaurants, Bars, ATMs, Bicycle racks, Farmers’ market, Shops, Toilets + Showers, Left luggage, Internet, Bureau de Change
Departure lounge – including a dedicated Eurostar lounge

Travel: St Pancras International Railway Station
Coach + bus travel
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principals. Coach travel can be part of a package or as separate holiday or a mode of transport.
. Coach travel is often a multi-centre holiday, where people visit a number of places
. Coach day trips are popular to attractions and events.
. Coach trips can cheap travel option (or for those who do not like to fly) and are popular in the ‘grey market’.
. Coach travel between airports and cities and city to city is a cost effective way to travel
. Coaches have become more luxury with toilets, Wifi, onboard entertainment + refreshments.
Buses provide a cheap and convenient way to travel especially in large towns and cities where the service is regular. Rural areas have less frequent services.
Sightseeing tours – like Big Bus – provide ‘hop-on hop-off’ services as well as information about the city.
. Coach travel is often a multi-centre holiday, where people visit a number of places
. Coach day trips are popular to attractions and events.
. Coach trips can cheap travel option (or for those who do not like to fly) and are popular in the ‘grey market’.
. Coach travel between airports and cities and city to city is a cost effective way to travel
. Coaches have become more luxury with toilets, Wifi, onboard entertainment + refreshments.
Buses provide a cheap and convenient way to travel especially in large towns and cities where the service is regular. Rural areas have less frequent services.
Sightseeing tours – like Big Bus – provide ‘hop-on hop-off’ services as well as information about the city.
Coach + bus terminal
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principals. Coach travel may be domestic or international
. Waiting time tends to less at coach terminals than airports therefore less facilities are needed
. Facilities may include:
. Toilets
. Waiting rooms
. Wifi
. Shops – food and drinks
. Left luggage
. Bus terminals may have basic facilities like toilets, food and drinks outlets.
. People at bus terminal tend to only be there for short periods so require less facilities.
. Covered or indoor seating areas are provided
. Waiting time tends to less at coach terminals than airports therefore less facilities are needed
. Facilities may include:
. Toilets
. Waiting rooms
. Wifi
. Shops – food and drinks
. Left luggage
. Bus terminals may have basic facilities like toilets, food and drinks outlets.
. People at bus terminal tend to only be there for short periods so require less facilities.
. Covered or indoor seating areas are provided
Car travel
Key sectors of the travel + tourism industry: Transport principalsCar hire
Hire car (or rental) companies operate in most towns and cities. Some are local, others are national or international companies
. They offer:
. a range of vehicles to suit customer needs
. airport pickup and drop-off
. one way hire
. insurance cover
Taxis + Ubers
Taxis + Ubers are used primarily for short journeys. Tourists more likely to use taxis that they can hail in the road.
Taxis are also used for airport and railway station drop offs and pick-ups.
Private cars
Most domestic holidays + visits use cars as the primary mode of transport.
Private cars are the most convenient ways for most people but traffic congestion can be problem.
Hire car (or rental) companies operate in most towns and cities. Some are local, others are national or international companies
. They offer:
. a range of vehicles to suit customer needs
. airport pickup and drop-off
. one way hire
. insurance cover
Taxis + Ubers
Taxis + Ubers are used primarily for short journeys. Tourists more likely to use taxis that they can hail in the road.
Taxis are also used for airport and railway station drop offs and pick-ups.
Private cars
Most domestic holidays + visits use cars as the primary mode of transport.
Private cars are the most convenient ways for most people but traffic congestion can be problem.




















